
23 Jan The Longtail Guide to Digital Marketing Frameworks (The only one you will ever need!)
Digital Marketing strategy frameworks are key to defining, organizing and executing integrated digital marketing activities. Any Digital marketing framework is the combination of when how and where digital marketing should be deployed across any business problem. While multiple institutes, associations, book writers have developed custom digital marketing strategy frameworks, this Marathon Guide will cover the most prominent and widely used frameworks.
What is a marketing framework?
A marketing framework is a structured visual representation of key steps towards execution of your marketing plan. An effective digital marketing framework provides you with immediate benefits. Not only does it provide a clear guideline to all team members but also ensures that all activities tracked as per defined goals.
Importance of executing marketing through a standard marketing framework?
Marketing frameworks are like a pre-installed navigational compass which helps guide each of your next actions in the most optimized manner. Without that structure, you might not be able to direct your/teams’ energies into the most important tasks in an integrate manner. Here are some of the pointers for why marketing frameworks are critical to your execution plan:
1) Establishing overall marketing objectives (both internal & with vendors)
If you have been marketing for a while, it might not be news to you that the most difficult part of executing marketing is to have a common (agreed upon) set of objectives (and activity cadence) to review implementation and performance. A marketing framework provides the much-needed structure and agreement to make sure that each team works towards a common goal with well laid-out steps.
2) Leveraging a structured approach (built out of prior experience)
The best (and most popular) marketing frameworks have witnessed the test of time and deployed across multiple industries. This gives you the confidence that if you follow a structured path, it would automatically weed out a lot of redundant steps/bottlenecks which you might impact performance.
3) Executing marketing activities in a quantitative (and timely) manner
Typically, marketers rely on their own experience to define success metrics for any marketing implementation which is most qualitative in nature (unless the client is vigilant enough!). Marketing frameworks help provide much needed quantification to not only raise alarms in-between implementation but also ensure timely delivery.
4) Deciphering (and plugging) gaps right at the start of implementation
Mapping any gaps in process right at the start could be quite demanding- when you are already busy in many other tasks. Marketing frameworks take the onus of helping identify and highlight key gaps which are most likely to surface in coming weeks to help you weed them out at the earliest.
5) Benchmarking performance (project by project) on a standard scale
Finally, you as a marketer need to benchmark your performance (with each next implementation) to potentially improve upon it. With a marketing framework at hand it becomes easy to go back in time and study the improvements/lags in implementation across any step to revise benchmarks or even change-course before the next step.
Difference between a Framework and a Model
Most of the times a Framework is confused with a Model. Experts have developed multiple marketing models which are now a standard staple in the industry. Marketing’s Top 10 evergreen models include:
4Ps Model (Extended to 7Ps)
The 4Ps Model is the most staple of marketing frameworks which can even be called a synonym to the work ‘marketing’ itself. McCarthy classified various marketing activities into marketing-mix tools of four broad kinds that are Product, Price, Place, and Promotion. Clearly these four Ps are not the whole story anymore. If we update these we will arrive at three more marketing realities: People, Process, and Physical Evidence. Let us go through each one by one.
-
- Product – It is a produced item by your company possessing tangibility and attributes adding bundle of benefits to your target audience. You need to very clear what you are offering to your customers and target audience.
- Price – This refers to the cost that your customers are willing to pay, which is basically set keeping in mind your competitors price and offerings.
- Place – Once the product is produced & price is decided, it is important for your organisation to make sure that the product is available in the right place at the right time. For this your organisation needs to decide the channels of distribution and manage inventory accordingly.
- Promotion – It includes all the strategies and techniques that help communicate your product to your target audience. This is basically choosing the right tools and media that fit with what you are trying to achieve.
- People – A company’s people are the ‘face’ of the company and interact with the customers on daily basis. So the point to be noted is that the people of your company are given right training, empowerment, and motivation.
- Process – For the smooth, efficient, and customer-friendly journey it is important that your company follows the right processes behind the scenes to make that happen.
- Physical Evidence- This is that element of marketing mix where the customers can actually see or experience when they use the service or product offered by your company.

Source – (www.oxfordcollegeofmarketing.com)
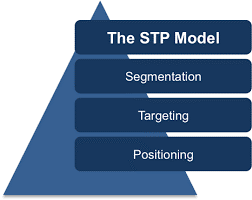
STP Model
STP stands for Segmenting, Targeting and Positioning is a broad framework with simplifies the process of Market Segmentation. So now, what is Market Segmentation exactly? It is a process, in which groups of buyers within a market are divided and profiled according to a range of variables, which determine the market characteristics and tendencies.
-
- Segmentation – The first and foremost step in the process of Market Segmentation is Segmentation which is identifying the market to be segmented and then segregating it on the basis of different variables depending on your company.
- Targeting – Once you have divided the market into different segments, your next job is to identify the most attractive segment from the segmentation stage. It is also called as Target market selection which helps you to direct the marketing activities of your company towards this group of target audience.
- Positioning – In this final stage, you focus on how your customers are ultimately viewing your products or services in comparison to your competitors. It is the perception by the target market about your offerings.
Source – (https://bit.ly/3fCDI4F)
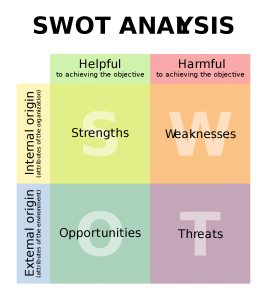
SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats) Analysis
In this VUCA world knowing how internal & external environment factors affect your company can help your business thrive. So let’s see how SWOT analysis helps your company in identifying these factors. SWOT analysis or situational analysis is a strategic planning technique used to help your company identify strengths, weakness, opportunities, and threats related to business competition. It is one of the important steps in goal setting for your company.
- Strengths – Strengths are the internal attributes of the company which are helpful to achieving your objectives. This basically gives answer to the questions like what do you well, what unique resources can you draw on & what do others see as your strengths.
- Weaknesses – These are the internal attributes of your company which are harmful to achieving the objective. It gives answers to the questions like what could you improve, where do you have fewer resources than others, what are others likely to see as weaknesses.
- Opportunities – Opportunities are the external conditions which are helpful to achieving your organisational objective. This basically gives answer to the questions like what opportunities are open to you, what special factors could you take advantage of & how can you turn your strengths into opportunities.
- Threats – These are the external conditions which are harmful to achieving the objective. It gives answers to the questions like what factors could harm you, what is your competition doing, and what threats do your weakness expose you to.
Source – (en.wikipedia.org)
PEST Model (Extended to PESTLE)
One of the most important analysis used to gauge external factors that could impact the profitability of your company.
-
- Political factors measures the degree of political stability and government intervention in economy.
- Economic factors includes factors like economic growth, exchange rates, inflation rates & interest rates. These have a great impact on your business and its expansion.
- Social factors have great impact on the buying patterns. It includes cultural aspects & health consciousness, population growth rate, age distribution, career attitudes, etc.
- Technological factors involves understanding technological advancements, rate at which technology gets obsolete. As we all know, technology changes very rapidly, it important to adapt accordingly because consumers are hungry to adapt.
- Legal factors have both internal & external sides. There are certain laws that affect your business environment in a certain country while there are certain policies that your company maintains for yourselves.
- Environmental factors include all those that influence or are determined by the surrounding environment and may affect your organizations policy.

Source – (www.pestanalysis)
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
Have you ever thought what motivates human behaviour? Maslow’s hierarchy of needs is one of the best-known theories of motivation. This theory of psychology that explains that humans are highly motivated in order to fulfil their needs, which is based on hierarchical order. Let’s looks at the needs one by one:-
-
- Physiological needs – These are the needs that are vital for your survival, like Food , water, breathing, sex, sleep, homeostasis, excretion, etc.
- Safety needs – We all know that people want control and order in their lives. Here the primary concern of us is related to safety and security.
- Belonging needs – Humans are social beings and they crave for being appreciated. In this stage, human behaviour is driven by emotions and the need for making emotional relationships is dominant here.
- Esteem needs –Having others recognise your achievements and a sense of your status in your career are all aspects of esteem needs. It deals with getting recognition, self-respect in the society.
- Self-Actualization needs – It is the highest level of needs and is known as the self-actualization needs. It relates your need to attain or realise the full potential of your ability or potential.

Source – (https://bit.ly/3nEt6Xs)
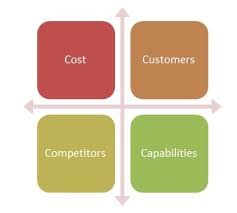
4Cs Model
The 4c’s of marketing are a commonly-used situation analysis technique used to help you make informed business decisions. Let’s us look at it one by one:-
-
- Costs – Instead of thinking of price, think of what your customer has to pay. Price is only a part of the total cost to satisfy a want or a need. The total cost will also consider, for example, the cost of time in acquiring a good or a service or a cost of conscience caused by consuming it.
- Customers – It is the value that you provide that determines your position in the sector or market/s. A company will only sell what the consumer specifically wants to buy. So, you should study consumer wants and needs in order to attract them one by one with something he/she wants to purchase.
- Competitors – The next step is to investigate opportunities to achieve differentiation and pre-empt competitor moves. Understanding your competitors is as important as understanding your own business. You’ll probably want to focus on companies similar in size to your own, but it’s OK if your competitors are larger or better-established than you – while it might not seem that way at first, smaller companies have a number of advantages over larger companies. The key to beating a larger competitor is to focus on small, attainable wins, and let those accumulate over time.
- Capabilities – The fourth, and often overlooked, “C” – capabilities – considers strategies that best fit with the business unit’s core competencies. You should be clear about make or buy decision that is what products should your business unit make itself, and what products should it buy from another company?
Source – (https://bit.ly/33Hz2Yx)
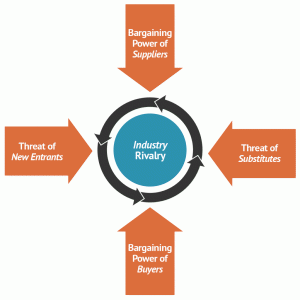
Porter’s Five Force
Porter’s Five Forces is a model that identifies and analyses five competitive forces that shape every industry and helps determine an industry’s weaknesses and strengths. Five Forces analysis is frequently used to identify an industry’s structure to determine corporate strategy. You will see that each of the five forces are able to affect the profit potential in the industry both positively and negatively.
-
- Competition in the industry– This is determined by the number of competitor, size of existing competitors, industry growth, product differentiation, and exit barriers.
- Number & Size of existing competitors, Industry growth- Rivalry is high when there are many competitors that are roughly equal in size and power when the industry is growing slowly which increases the fight for market share.
- Product Differentiation -When competitors are not much differentiated from each resulting in products & services nearly identical.
- Exit barriers- In addition rivalry will be more intense when the barriers to exit are high, forcing companies to remain in the industry even though profit margins are declining.
- Potential of new entrants into the industry– New entrants put pressure on your current organization within an industry through their desire to gain market share. A company’s power is also affected by the force of new entrants into its market. The less time and money it costs for a competitor to enter a company’s market and be an effective competitor, the more an established company’s position could be significantly weakened.
- Power of suppliers – The bargaining power of suppliers is also described as the market of inputs. Suppliers of raw materials, components, labour, and services (such as expertise) to the firm can be a source of power over the firm when there are few substitutes. For example, if you are making cookies and there is only one person who sells flour, you have no alternative but to buy it from them. Suppliers may refuse to work with your firm or charge excessively high prices for unique resources.
- Power of customers – The bargaining power of customers is also described as the market of outputs: the ability of customers to put the firm under pressure, which also affects the customer’s sensitivity to price changes. You can take measures to reduce buyer power, such as implementing a loyalty program. Customers’ power is high if they have many alternatives, and it’s low if they have few choices.
- Threat of substitute products- So what exactly is Substitute product? A substitute product uses a different technology to try to solve the same economic need. Say, for example ink pen and ball pen, both serve your purpose of writing on a paper.
- Competition in the industry– This is determined by the number of competitor, size of existing competitors, industry growth, product differentiation, and exit barriers.
Source –(https://bit.ly/3IiYzWS)
AIDA Model
AIDA Model is a way of thinking about your customers’ purchase decisions in terms of Awareness, Interest, Desire, and Action across a marketing funnel:
-
- Attention – The first stage of AIDA model is attention. This means that through your promotional activities you want to try to sort of move customers through those stages. So the first thing you need to do to get customer to buy your product is you need to get their attention, in other words you need to make them aware of your offerings.
- Interest – If you want your target audience to buy your product it is not just enough for them to know about your product, they have to be interested in what you have to offer. So you have to communicate the benefits of your brand or your product to the audience.
- Desire – The next stage is desire, so you have got the attention from your target audience, now you have to entice them towards your product, this can be done through advertising about your product’s pros and how it will benefit your target audience. Offering limited time offers and discounts will also boost the desire for the product.
- Action – The final stage is action, where you ultimately tip your target audience over to persuade them to buy your product, you also make sure that the process of them purchasing it is as smooth as possible.
BCG Matrix
Boston Consulting Group matrix or Growth share matrix is a portfolio management framework that helps your company to decide how to prioritize your different businesses by your degree of profitability. The matrix reveals two factors that you should consider when deciding where to invest—company competitiveness, and market attractiveness—with relative market share and growth rate as the underlying drivers of these factors. Each of the four quadrants represents a specific combination of relative market share and growth. Let’s understand these one by one:-
-
- Low Growth, High Share –Cash cows, seen in the lower left quadrant, are products that are in low-growth areas but for which the company has a relatively large market share. You should milk these “cash cows” for cash to reinvest.
- High Growth, High Share – Stars, seen in the upper left quadrant , are products that are in high growth markets and that make up a sizable portion of that market. You should significantly invest in these “stars” as they have high future potential.
- High Growth, Low Share – Question marks, seen in the upper right quadrant, they typically grow fast but consume large amounts of company resources. You should analyse products in this quadrant frequently and closely see if they are worth maintaining.
- Low Growth, Low Share – Dogs, seen in the lower right quadrant , are products that have a low market share and is at a low rate of growth. These products don’t generate much cash for your company since they have low market share and little to no growth. You should liquidate, divest, or reposition these “pets.”
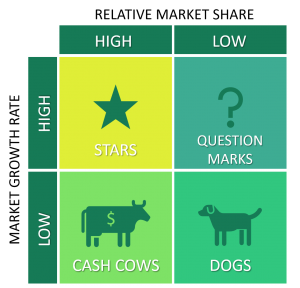
Source – (https://www.business-to-you.com)
Ansoff Matrix
The Ansoff matrix is a strategic planning tool that provides a framework to help you devise strategies for future growth. The matrix combines market penetration, market development, product development, and diversification, which are all growth alternatives that your organization can use to effectively grow its reach into other markets or grow its product offerings.
-
- Market Penetration-It’s when your organization attempts to grow in a market it already exists in with products, services or other offerings it already has. The goal of market penetration for your organization to increase its market share by finding new customers in the same market or selling more of its offerings to an existing customer base. So how can you do this? You can penetrate in the market by increasing promotional efforts, decreasing prices, etc.
- Market Development-It’s when your organization uses its current offerings and attempts to grow into other markets. The development of new markets for the product may be a good strategy if the firm’s core competencies are related more to the specific product than to its experience with a specific market segment.
- Product Development- This is a stage when an organization creates new offerings for its existing market. A product development growth strategy is about as risky as the market development strategy. With this strategy, your organization will have an expanded product line that customers can choose from.
- Diversification-In diversification your organization tries to grow its market share by introducing new offerings in new markets. It is the most risky strategy because both product and market development is required. One of the advantages of diversification includes the potential to gain a foothold in an attractive industry and the reduction of overall business portfolio risk.
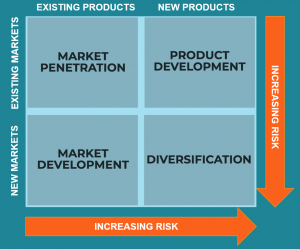
Source – (https://corporatefinanceinstitute.com)
Marketing frameworks: How are they classified?
Marketing frameworks can be classified right from the start of establishing a goal, executing market analysis, deciding customer mix, developing brand and communications strategy. Multiple frameworks have historically been developed for specific marketing. Let us look at them and study their inherent top five models each:
1. Goal Setting Frameworks
S.M.A.R.T Goals
Probably the most deployed Goal Setting framework across the world, the S.M.A.R.T acronym stands for Specific, Measurable, Actionable, Relevant, and Timely. It can be used to help evaluate and add structure to your goals. Let’s understand these one by one:-
-
- Specific– This is the most important part of establishing or evaluating a goal, the less specific a goal the more difficult it is to determine how long the goal should take to complete or how to measure success.
- Measurable-So what determines success? There are some goals that may be measured by a simple yes-no, while other goals are better measured by using metrics. The key here is making sure that in whatever way the goal is measured, it accurately measures success.
- Actionable– Actionable means asking how your goal will be achieved. Here you should check whether you have the resources and capabilities required to achieve success or not. Just keep in mind here that well-designed goals provide clarity of action.
- Relevant– A common issue you might face, is having too many goals at the same time or pursuing the wrong goals. Through this framework, you need to monitor your goals to make sure that you are pursuing your most relevant goals at any given moment in time.
- Timely– The last thing you want to make sure is that your goals are time-bound. By providing a specific timeline by which your goal should be accomplished, it helps provide incentive and monitor progress.
It is important to reinforce that goal-setting is not an event, it is an ongoing process of action, evaluation, and revision.

Source – (https://www.hydratemarketing.com)
OKRs
OKRs stand for Objective and key results are a collaborative goal-setting tool. But what exactly means by OKR? In order to have a shot at accomplishing your goals, you need to have a way to measure your progress and achievement. And this is where the OKR framework comes in.
-
- The objective is the direction. Your primary goal. And it answers the question “What you’re trying to achieve?”
- The key results are the benchmarks to track your progress. They are the metrics of your success. And it answers the question “How will you accomplish it?”
Objectives set the direction that you’re heading in and should not contain a metric while key results often provide the measure to gauge that progress. So the essence of this framework is to set challenging or ambitious goals with measurable results. It helps in providing clarity, enhanced communication and a coherent, transparent organization-wide strategy.

Source – (https://bit.ly/3nEkNuG)
4DX
There are four disciplines that make up a system of execution that can help you reliably execute no matter how chaotic the world gets around you. Let’s look at the disciplines:-
-
- Focus on your W.I.G. – You need to keep all your urgent and merely important goals on your radar. Do the minimum to maintain the urgent & less important tasks. Next thing is use your remaining energy to execute one wildly important goal.
- Measure Lead Behaviours – We need to measure something that we can influence and improve every day or every week. So what we need to measure here is our lead behaviour. These are the regular day to day activities that ultimately lead to your desired result.
- Put up a scoreboard – You should know what you are up to, when you are aware of how far you have come, you will automatically be able to know where you have to go.
- Schedule weekly accountability talks- You need to make verbal commitments with your teammates so that you can allot the responsibilities. This will also ensure that everyone in the team is one the same page.
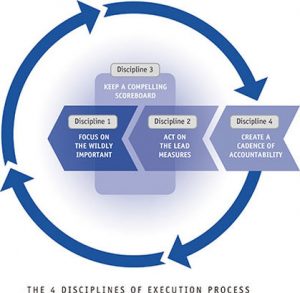
Source – (https://mrswatsonsweb.weebly.com)
Locke and Latham’s 5 principles
This theory is used for setting goals for yourself or your team. As we know that the right goals can increase motivation and productivity. When you set challenging goal and receive regular feedback on your progress, then your productivity and motivation will increase. So, you need to have clarity in your goals. We will now see the 5 principles in Goal Setting that will help you increase productivity
-
- Clarity-To keep you motivated, your goals need to be clear. You need to understand how you will know you have hit your goal. Here you can take reference from SMART goals that we discussed earlier.
- Challenge– Next, your goal should be challenging, but keep in mind it should not be too challenging. To keep you motivated, your goal must hit the sweet-spot between challenging you but not over challenging you.
- Commitment– For a goal to be challenging, you must be committed to it. As a team you and your team members should determine the targets together and how you hit them if you do that.
- Feedback– You should welcome both positive and negative feedbacks, so that you can work on your negatives and also know what you are good in and keep moving ahead with it. You can have weekly check-ins etc to receive feedback.
- Task Complexity – Your goals should not be too complex, as they can be overwhelming and even demotivating. So what you can do here is to break complicated tasks down into sub targets.Locke and Latham’s 5 principles – This theory is used for setting goals for yourself or your team. As we know that the right goals can increase motivation and productivity. When you set challenging goal and receive regular feedback on your progress, then your productivity and motivation will increase. So, you need to have clarity in your goals. We will now see the 5 principles in Goal Setting that will help you increase productivity.
So goal setting, when done correctly can be a powerful tool for boosting motivation & production.
 Source – (https://bit.ly/3nCiGHC)
Source – (https://bit.ly/3nCiGHC)
2. Consumer Marketing Frameworks
Customer Lifetime Value
CLV is a measurement of how valuable a customer is to your company, not just on a purchase-by-purchase basis but across the whole relationship. It is a great metric to use when you have a multi-year relationship with a customer and it’s good for spotting the early signs of attrition – say, for example, you see spend dropping off after the first year as they use the subscription less and less. You can measure CLV in the following way:-
-
- You need to identify the touchpoints where your customer creates the value.
- Integrate records to create the customer journey.
- Measure revenue at each touchpoint.
- Add together over the lifetime of that customer.
Loyalty Ladder Model
As the name suggests, the loyalty ladder model sees your customers gradually moving up through relationship levels, starting at the bottom as prospects (those who have the intent to purchase your product but have not yet done so) and ending up at the top as advocates (intensely loyal brand champions).
-
- Prospect is someone whom you believe may be persuaded to do business with you.
- Customer is someone who has done business just once with your organisation.
- Client is the one who has done business with you on a repeat basis but may be negative, or at best neutral, towards your organisation.
- Supporter is someone who likes your organisation, but only supports you passively.
- Advocate is someone who actively recommends you to others, in other words, who does your marketing for you.
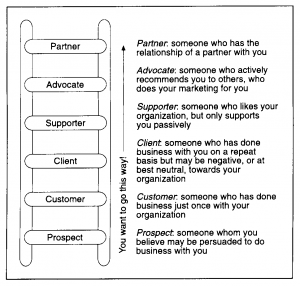
Source –(https://juanjosedelgado.wordpress.com)
Consumer Decision Making
All consumers go through basic steps when making a purchase to determine what products and services will best fit their needs and this process is known as Consumer Decision Making. Customers consider what they need, research, and compare options available before taking the plunge. Let’s us look at the steps one by one for better understanding:-
- Problem recognition– The first step of the consumer decision-making process is recognizing the need for a service or product.
- Information search – Once consumers recognize a want, they need to gather information to understand how they can fulfill that want.
- Alternatives evaluation – At this point, prospective buyers have developed criteria for what they want in a product. Now they weigh their prospective choices against comparable alternatives.
- Purchase – During this stage, buying behaviour turns into action – it’s time for the consumer to buy! If you’ve done your job correctly, the consumer will recognize that your product is the best option and decide to purchase.
- Post-purchase evaluation – Once the purchase has been made, is it above or below your customers’ expectations? Your goal should not be for a one-time customer but a repeating lifetime customer.
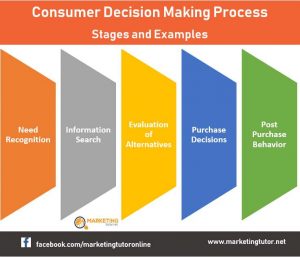
Source-(https://www.marketingtutor.net)
Customer Journey Framework
A customer journey is an entire experience a customer has while communicating with your brand. It considers the complete interaction roadmap from brand discovery to purchasing and beyond. Awareness, Consideration, and Conversion are the three steps that make up Customer Journey experience. Let’s look at these one by one:-
-
- Awareness– This involves spreading general information about your products and services to your target audience.
- Consideration-This is where customers begin to look for alternatives to past purchases. During this phase, your business strives to convince your potential buyers to include you in their list of available options.
- Conversion– Using a dedicated call-to-action, you encourage customers to make a purchase, subscribe to a mailing list, or sign up for services. You should use this phase to sell your product as the best fit to solve a visitor’s problem.
Customer Experience Framework
Customer experience framework is a set of tools and procedures that you can put in place to ensure exceptional CX. These are the three building blocks of customer experience transformation.
-
- Build aspiration & purpose – The first step you need to do is to align on a crisp definition of the type of experience you want to deliver. You should be very clear regarding what you want your customers to feel.
- Transform the business- You need to identify the core journeys, what are the journeys for your customer that actually matter.
- Enable the transformation- Once you have identified the core journeys then you need to think of enabling the transformation. Think of it like how can you redesign the transformations.
3. Brand Strategy Frameworks
This is a map for achieving long-term goals that don’t always need a discrete endpoint. Brand strategy is more like a process or a path that involves moving iteratively towards your goals.
Brand Architecture Framework
It’s the structure of brands within an organizational entity. It is the way in which the brands within a company’s portfolio are related to the overall portfolio or whether it’s differentiated. We can understand it like whether the brand wants to go for Multi- Branding or Umbrella Branding?
-
- Umbrella Branding – It is a marketing practice involving the use of a single brand name for the sale of two or more related products. As you are promoting a single brand there is lower advertising, imagery, and communication costs. One more thing here is, if you are good at customer satisfaction, it transfers to your other units.
- Multi Branding – You can use this strategy to appeal to different market segments or categories. Here, you will be able focus on verticals better.
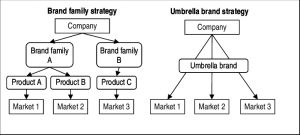
Source- (https://www.researchgate.net)
Brand Personality Framework
Brand Personality describes brands in terms of human characteristics. You have to decide what personality traits your brand is to have. There are various ways of creating brand personality. One way is to match the brand personality as closely as possible to that of your consumers or to a personality that they like. The process that you can follow here is:-
- You need to define your target audience
- Then next step is to find out what they need, want, and like
- Build a consumer personality profile
- Create the product personality to match that profile
Source – (https://bit.ly/3rynJdk)
Brand Messaging Framework
It explains the story of how you were founded, along with the reason why your product/service is important and needed. Brand Messaging conveys the emotion behind your brand. It ensures that your advertising, marketing, sales, and support teams are all on the same page. So now let’s see how you can create your Brand Messaging Framework:-
-
- Your Mission statement- It explains the reason why you created your product/service. You usually have to use one line to communicate the same.
- Your Tagline- A tagline should explain your mission statement in more detail.
- Your Value Proposition- This gives the answer to the question “What makes you the best company to solve that problem?” Your value proposition is why to your mission statement.
- Core brand pillars- These are the real impacts that someone can experience as a result of using your product.
Brand Positioning Framework
Brand positioning is the process of positioning your brand in the mind of your customers. It is used to set your business apart from the rest. There are 7 types of Brand Positioning Frameworks:-
-
- Customer Service Positioning Strategy- Here your main focus is customer service. The most tangible benefit of this strategy is that great customer service can help justify a higher price point.
- Convenience-based Positioning Strategy- This highlights why your company’s product or service is more convenient to use than the competitions. Positioning your product or service as the most convenient will automatically attract busy consumers.
- Price-based Positioning Strategy – When you position your product as the cheapest on the market, you can generate a large customer base because no one likes to spend more than they have to. Offering the lowest price is an easy way to get prospects to convert.
- Quality-based Positioning Strategy- You can implement this strategy when you want to emphasize the quality of your product —quality that often comes at a premium cost.
- Differentiation Strategy- This strategy relies on your product’s uniqueness or innovative qualities in comparison to your competition.
- Social Media Positioning Strategy- When using this strategy, the key is to choose the channels your target market uses the most. Your brand doesn’t have to show up across each platform.
- Other Positioning Strategy – You can position your brand as the leader, the first of its kind (the original), or the most popular. You can also position your product as the solution to a pervasive problem.
4. Communication Frameworks
Communication Strategy
As the name suggests, a communication Strategy Framework clarifies how your business should communicate with your employees, investors, customers, and suppliers. This is one of the important framework as the success of your organisation is dependent upon the individuals within your organisation and how well they communicate with internal & external stakeholders. It helps you align company values, goals, and objectives with behaviours that contribute to long-term success.
Let’s now look at the components:-
-
- Purpose is a brief statement regarding the communication strategy and how you are going to implement it.
- Background is a description of your initiative.
- Objectives – Your company communications should be in alignment with your company objectives.
- Target Audience – You should keep your target audience in mind & then create the strategy accordingly.
- Messaging – Here you might have to do a little research and create a robust strategy which your target audience wants to hear and how they want to hear it. You should research your audience and then craft a story that is concise and relatable.
- Approach – Here you try to find answer for how will your strategy be implemented?
Integrated Marketing Communication
Integrated Digital Marketing Framework is the process of conveying a unified message across a variety of channels to drive higher customer engagement for your company’s products and solutions. The five primary tools for Integrated Marketing Communication are:-
-
- Advertising- If you want to reach larger audiences quickly, this is an effective way to communicate. Although this might cost you a bit more because of its wide reach. These can be seen in print, posters, TV, radio, etc. You have choose the medium based on your target audience.
- Direct Marketing- It focuses on presenting your brand information to only those with similar interests. Like telemarketing, EDM marketing, brochures, and online targeted display ads.
- Internet Marketing– These include marketing on variety of online platforms, tools, and content delivery systems used to market products and services online and through other digital means.
- Sales Promotion- This is a marketing strategy where the product is promoted using short-term attractive initiatives to stimulate its demand and increase its sales. It helps you to spread information about your brand to new customers or market.
- Public Relations- refers to managing how others see and feel about your company. So how is PR different from advertising? PR differs from advertising in that PR attempts to represent your company’s image in ways that will appear organic.
5 Ws of Communication
To make your communication on point it is required that you are clear with the following Ws while making your communication strategy.
-
- Who will communicate in customer service?
- What will be communicated in customer service?
- When should it be communicated?
- Where will customer service take place?
- Why will you implement customer service?
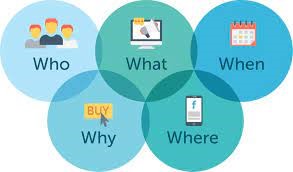
Source – (https://bit.ly/3fyUX73)
Apart from the above specific area-wise Frameworks have also been developed. Let us review key constituent models across each of these framework areas:
B2B Marketing Frameworks
B2B Marketing Strategy Framework
This framework will allow you to:-
-
- Use research to make data-driven decisions about marketing campaign targeting and be able to back up tactics to your leadership team.
- Gain a full understanding of your market and ideal customers to bring more relevant traffic to your website.
- Develop messaging that resonates with your ideal buyers.
- Build a brand and brand assets that are credible and impactful to potential prospects
B2B Sales Strategy Framework
In order to develop a B2B sales strategy framework you should, understand your customers, develop value proposition, equip your team, get right tools and determine key activities.
B2B Segmentation Framework
Here you follow the following steps to segment and target your audience:-Target Prospects –
-
- Prioritize specific customers
- Refine marketing messages
- Optimize channel strategies
- Develop right content
- Optimize proposition
- Allocate budget
B2B Content Strategy Framework
The primary goal of the B2B content strategy is to get the service pages to rank for commercial-intent phrases. Let’s look at 7-part content strategy framework for B2B lead generation built for SEO.
-
- The Core – At the centre of all digital marketing is the sales page. It is built to attract and convert qualified visitors.
- The Mission – Next, you need to lay the cornerstone of our content marketing is the content mission statement. It declares your target audience, the topics to be published and the benefits of the content to your audience.
- Publish Research – Next, you need to beat every content program in our industry by being more relevant, useful, and original. Focus on conducting & publishing original research.
- Write for current prospects– The best source for content ideas is the audience themselves. When you talk to prospects and customers, you learn their cares, hopes and worries. You find out what questions they have. It’s the job of your content to answer their questions.
- Using Visuals – For making your content strategy successful use visual formats regularly.
- Collaborate with influencers – Collaborating with content creators is powerful, partly because it supports your long term goal of building your authority. The idea is partly to make your brand and your content more visible to people who create content.
- PR Focus– In the process of building an audience, guest blogging and digital PR are so important.
B2B Customer Experience Framework
Customer experience framework is a set of tools and procedures that you can put in place to ensure exceptional CX. These are the three building blocks of customer experience transformation.
-
- Build aspiration & purpose – The first step you need to do is to align on a crisp definition of the type of experience you want to deliver. You should be very clear regarding what you want your customers to feel.
- Transform the business- You need to identify the core journeys, what are the journeys for your customer that actually matter.
- Enable the transformation- Once you have identified the core journeys then you need to think of enabling the transformation. Think of it like how can you redesign the transformations.
Product Marketing Frameworks
The Product Management Framework
Product development frameworks are the sets of steps that consist of conceptualization, design, development, and marketing of specific goods or services.
Product Strategy Framework
Your product strategy is the roadmap that’s used to develop your product or feature. It includes all of the tasks that your team needs to complete to achieve your business goals.
-
- Cost Strategy – A cost strategy focuses on creating the best product for the lowest price
- Differentiation Strategy- Price isn’t the end-all-be-all when it comes to differentiating your product. There are plenty of other ways that you can make it stand out in your industry.
- Focus Strategy – Here you select a particular focus group, this is an effective strategy because here you target the needs of a select group of people and creates a personalized solution for them.
- Quality Strategy- Sometimes what can set your item apart from competitors could be the make and brand behind it. Quality strategy focuses on the customers who are looking for the highest quality product in the market.
- Service Strategy– By providing quick response and better after-sales service, brand loyalty in any market can be built to last.
Source – (https://bit.ly/3KA9PAr)
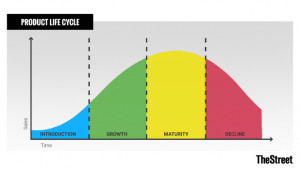
Product Lifecycle
The product life cycle is the process a product goes through from when it is first introduced into the market until it declines or is removed from the market. The life cycle has four stages—introduction, growth, maturity, and decline. Once a product is developed, it typically goes through the four stages of the product life cycle—from introduction through decline—before eventually being retired from the market.
Source – (https://bit.ly/32fdpOY)
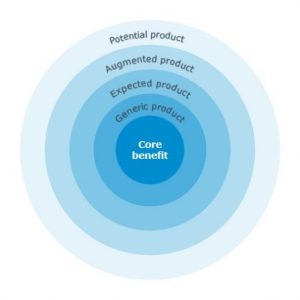
Kotler’s Five Product Levels
-
- Core Product – This is the basic product and the focus is on the purpose for which your product is intended.
- Generic Product– This represents all the qualities of your product.
- Expected Product – This is about all aspects the consumer expects to get when they purchase a product. This answers the question what qualities should your product have?
- Augmented Product – It refers to all the additional which sets the product apart from that of the competition. This particularly involves brand identity and image.
- Potential Product – This is about augmentations and transformations that your product may undergo in the future
Source – (https://bit.ly/3fEFiCZ)
Product Development Framework
The product development process encompasses all steps needed to take your product from concept to market availability. This includes identifying a market need, researching the competitive landscape, conceptualizing a solution, developing a product roadmap, building a minimum viable product, etc.
-
- Ideate- This is where your team shares all of its innovative ideas.
- Research- Here, you validate your idea with potential users, and review competitive offerings.
- Plan- After sourcing suppliers, estimating the production budget here you determine how to price your product.
- Prototype– Now you develop a sample of your finished product to share with key stakeholders.
- Source – Putting together your plan for vendors, materials, and other resources needed to turn the successful prototype into a mass-market product.
- Cost- Here you document all of the costs required to bring the product to market.
Service marketing frameworks
Service Management Framework
Service management frameworks describe the essential activities of good service management as processes or practices.
The Service Design Framework
Service design a framework is a way of navigating and communicating complexity.
Service Delivery Framework
A service delivery framework (SDF) is a set of principles, standards, policies, and constraints to be used to guide the designs, development, deployment, operation, and retirement of services delivered by a service providerwith a view to offering a consistent service experience to a specific user community in a specific business context
The Service Excellence Framework
It provides a whole-of-company capability development roadmap for organisations, so companies can create and define their desired service experience.
Service Assurance Framework
Service assurance is an all-encompassing paradigm that revolves around the idea that maximizing customer satisfaction inevitably maximizes the long-term profitability of an enterprise.
Growth Strategy Frameworks
Growth Strategy Matrix
Growth strategy matrix shows four strategies you can use to grow your business. It also helps you analyse the risks associated with each one. It’s same as Ansoff Matrix that we discussed earlier. The four strategies are as follows:-
-
- Market Penetration
- Market Development
- Product Development
- Diversification
Growth and Transformation Framework
It represents the growth rate of a product and its potential to grow in a particular market.
The Growth Mind-set Framework
The idea behind growth mind-set is that, by identifying new opportunities, you will be able to build a highly engaged audience.
Growth Hacking Framework
It is the process of continually optimizing the growth of a key business metric. That metric could be weekly active users (WAU), lifetime value (LTV), profit, revenue, or any other number that indicates success for your business
The Start-up Pyramid
Start-ups require a solid foundation of product/market fit before progressing up the pyramid and scaling the business.
-
- Product/ Market fit – Customer Validation proves that you have found a set of customers and a market who react positively to the product
- Transition to growth – Here you highlight the benefits described by your “must have” users and Implement the business model that allows you to profitably acquire the most users.
Pirate Metrics
Pirate metrics are a way to categorize and group together metrics depending on what aspect of the business you want to measure. The parameters are as follows:-
-
- Acquisition – How are people discovering your product or company?
- Activation- Are these people taking the actions you want them to?
- Retention- Are your activated users continuing to engage with the product?
- Referral- Do users like the product enough to tell others about it?
- Revenue- Are your personas willing to pay for this product?
Lean Analytics
Lean Analytics is used to measure that progress, helping you ask the most important questions and get clear answers quickly. You should ask yourself a few questions before framing a business model like
-
- How customers buy your product?
- Why they purchase from you?
- At which stage of your business they are in?
- What is the budget of your customers?
Finally, you can also make use of one of the top Digital Marketing strategy-specific frameworks: ASCOR Digital marketing framework which provides a structured approach to Digital Marketing through a step-by-step deployment of digital marketing strategies.
Article Reference Links
- https://smallbusiness.chron.com/internal-external-environmental-factors-affect-business-69474.html
- https://www.investopedia.com/terms/p/pest-analysis.asp
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Marketing
- https://blog.oxfordcollegeofmarketing.com/2020/10/08/understanding-the-7ps-of-the-marketing-mix/
- https://avada.io/resources/stp-marketing-model.html
- maslow’s hierarchy of needs – Bing
- Marketing Management – By Philip Kotler
- Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs – Kings Tutors
- Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs Theory (byjus.com)
- https://www.volusion.com/blog/situation-analysis-the-5-cs/
- https://www.mbaboost.com/4-cs-framework/
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Porter%27s_five_forces_analysis
- https://www.bcg.com/about/overview/our-history/growth-share-matrix
- https://www.investopedia.com/terms/b/bcg.asp
- com/strategy/matrix/ansoff/
- https://www.indeed.com/career-advice/career-development/ansoff-matrix
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ansoff_matrix
- https://www.eightleaves.com/2010/04/the-loyalty-ladder-a-sideways-look
- https://www.google.com/url?sa=i&url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.researchgate.net%2Ffigure%2FThe-Customer-Loyalty-Ladder_fig5_233960420&psig=AOvVaw08Y3P-R2651VqS5iJYLJxo&ust=1640259689688000&source=images&cd=vfe&ved=0CAsQjRxqFwoTCPDXwdOp9_QCFQAAAAAdAAAAABAD
- https://www.lucidchart.com/blog/consumer-decision-making-process
- https://www.questionpro.com/blog/customer-journey-map/
- https://visme.co/blog/brand-strategy/
- https://fourweekmba.com/communication-strategy-framework/
- https://www.thebalancesmb.com/internet-marketing-2948348#:~:text=Internet%20marketing%20refers%20to%20the,Social%20media
- https://www.investopedia.com/terms/p/public-relations-pr.asp
- https://www.google.com/imgres?imgurl=https%3A%2F%2Fexpertprogrammanagement.com%2Fwp-content%2Fuploads%2F2018%2F10%2FLockes-Goal-Setting-Theory.png&imgrefurl=https%3A%2F%2Fexpertprogrammanagement.com%2F2018%2F10%2Flockes-goal-setting-theory%2F&tbnid=a8CAEeQ10GHehM&vet=12ahUKEwiXy5373Pv0AhU4gmMGHaYECToQMygFegUIARCMAQ..i&docid=b2nc437T7nAiKM&w=640&h=500&itg=1&q=%E2%80%A2%09Locke%20and%20Latham%E2%80%99s%205%20principles%20&ved=2ahUKEwiXy5373Pv0AhU4gmMGHaYECToQMygFegUIARCMAQ
- https://coschedule.com/blog/brand-messaging-framework-template
- https://blog.hubspot.com/sales/brand-positioning-strategy
- Concepts of Brand Management – Rai Technology University
- https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/b2b-marketing-strategy-framework-step-guide-alex-avendano
- https://www.demandcurve.com/article/growth-hacking#:~:text=Growth%20hacking%20is%20the%20process,indicates%20success%20for%20your%20business.
- https://www.productplan.com/glossary/aarrr-framework/
- https://www.educba.com/lean-analytics/
- https://www.cgma.org/resources/tools/cost-transformation-model/kotlers-five-product-level-model.html
- https://www.cgma.org/resources/tools/cost-transformation-model/kotlers-five-product-level-model.html
- https://birdeye.com/blog/customer-experience-framework/
- https://www.productplan.com/glossary/product-development-process/
- https://cadabra.studio/blog/product-management-frameworks-for-project-development
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Service_delivery_framework
- https://www.ssg.gov.sg/wsq/Industry-and-Occupational-Skills/Service-Excellence-Competency-Framework.html
- https://searchcustomerexperience.techtarget.com/definition/service-assurance-SA

No Comments